Evidence of Evolution Worksheet. Evidence of Evolution Worksheets are a valuable educational tool for both teachers and students. These worksheets provide a comprehensive overview of the evidence that supports the theory of evolution, and they’re designed to be interactive and engaging. Teachers can use these worksheets to help their students learn about evolution, and students can use them to reinforce their understanding of the topic.
The best part about Evidence of Evolution Worksheets is that they’re available in both PDF and DOC format. This means that you can either print out the PDF version for a traditional, paper-based learning experience, or you can download the editable DOC version and edit it using Microsoft Word or Google Docs. This versatility makes Evidence of Evolution Worksheets a perfect tool for any type of learning environment, whether it’s in a classroom or at home.”
Furthermore, As I study these worksheets, I found that Comparative anatomy is a method of classification that encompasses both plants and animals. This type of classification provides valuable insight into the process of evolution, as it compares the anatomy of different species to determine their evolutionary relationships. This is known as anatomical evidence of evolution. There are various resources available to help understand this concept, such as the evidence of evolution worksheet (doc and pdf formats), the evolution worksheet answer key, the darwin theory of evolution pdf answer key, and an evidence of evolution quiz pdf. Additionally, students can find evidence of evolution worksheet answers on quizlet to test their understanding of the topic.
Download The Evidence of Evolution Worksheet
Coverage: Evidence of Evolution, Fossils, Similarities between skulls, Change in skull anatomy, Change in leg anatomy, Embryology, Physical similarities between embryos, Common ancestor between organisms, Ontogeny recapitulates Phylogeny, Comparative Anatomy, Skeletal structure of front limbs, Primary functions of animal limbs, Comparison to human arm in form and function.
Terms used: Evidence of Evolution, Biology, Basic idea of natural selection, evolutionary adaptation, genetic makeup, five lines of evidence, fossil record, biogeography, comparative anatomy, comparative embryology, molecular biology, Charles Darwin, theory of natural selection, mutations, review, textbook, evidence of evolution worksheet, skulls, leg fossils, horse, Equus, Pilohippus, Merychippus, Mesohippus, Eohippus, embryology, physical similarities, embryos, human, chicken, rabbit, tortoise, salamander, fish, anatomical changes, physical similarities, common ancestor.
Some Questions:
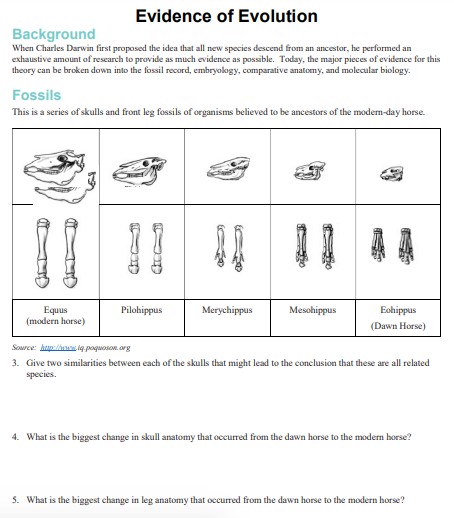
- Give two similarities between each of the skulls of organisms believed to be ancestors of the modern-day horse.
- What is the biggest change in skull anatomy that occurred from the dawn horse to the modern horse?
- What is the biggest change in leg anatomy that occurred from the dawn horse to the modern horse?
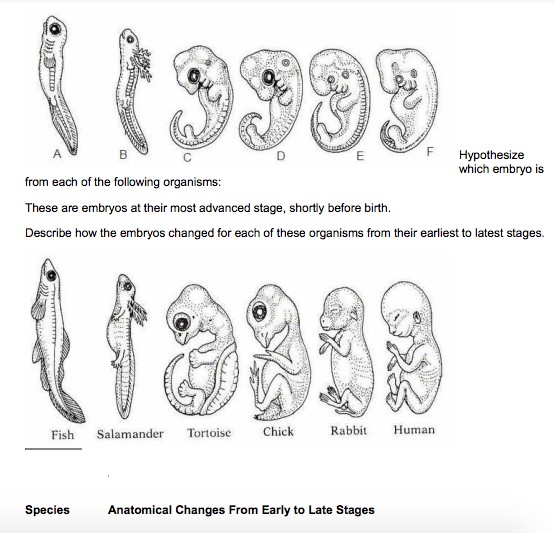
- Hypothesize which embryo is from each of the following organisms: Human, Chicken, Rabbit, Tortoise, Salamander, and Fish in their earliest and most advanced stages.
- Describe how the embryos changed for each of these organisms from their earliest to latest stages.
- Describe the physical similarities between the embryos in their earliest stages.
- Explain how the embryos can be used as evidence of a common ancestor between each of the six organisms.
Key Terms:
Evidence of Evolution, Background, Charles Darwin, new species, ancestor, research, theory, fossil record, embryology, comparative anatomy, molecular biology, Equus, modern horse, Pilohippus, Merychippus, Mesohippus, Eohippus, Dawn Horse, similarities, skulls, related species, biggest change, skull anatomy, leg anatomy, older, developed embryos, physical similarities, common ancestor, skeletal structure, front limbs, human, crocodile, whale, cat, bird, bat, Humerus, Ulna, Radius, Carpals, Metacarpals, Phalanges, Primary Functions, tool use, holding objects, comparison, form, function, butterfly, bird wing, body structure, cave fish, minnow, eyesight, sensory adaptation, Homologous structures, individual variations, Analogous structures, different anatomies, similar functions, Vestigial structures, remnants, important, no longer used.
Instructions:
- Instructions for the fossil record section:
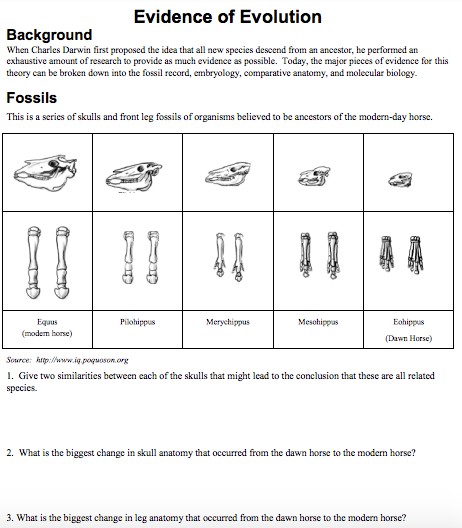
- Give two similarities between each of the skulls that might lead to the conclusion that these are all related species.
- What is the biggest change in skull anatomy that occurred from the dawn horse to the modern horse?
- What is the biggest change in leg anatomy that occurred from the dawn horse to the modern horse?
- Instructions for the embryology section:
- Hypothesize which embryo is from each of the following organisms:
- Human
- Chicken
- Rabbit
- Tortoise
- Salamander
- Fish
- Describe how the embryos changed for each of these organisms from their earliest to latest stages.
- Look again at the six embryos in their earliest stages. Describe the patterns you see. What physical similarities exist between each of the embryos?
- Does this suggest an evolutionary relationship? Explain how these embryos could be used as evidence of a common ancestor between each of these six organisms?
- Hypothesize which embryo is from each of the following organisms:
- Instructions for the comparative anatomy section:
- Color code each of the bones of the skeletal structure of the front limbs of 6 animals: human, crocodile, whale, cat, bird, and bat.
- Indicate what type of movement each limb is responsible for for each animal.
- Compare the skeletal structure of each limb to the human arm in form and function.
- Compare the anatomy of the butterfly and bird wing.
- What is the function of each of these structures?
- How are they different in form? Give specific differences.
- Compare the overall body structure of the cave fish and the minnow.
- What is the biggest, most obvious difference between the body structure of these two fish?
- Assume the two fish came from the same original ancestor. Why might the cave fish have evolved without eyesight?
- What kind of sensory adaptation would you hypothesize the cave fish has to allow it to navigate in a cave, including catching and eating food?
- Questions about homologous, analogous, and vestigial structures:
- Give an example of a homologous structure from this activity.
- Give an example of an analogous structure from this activity.
- Give an example of a vestigial structure from this activity.
- Explain the difference between homologous, analogous, and vestigial structures.

Sample Questions and Answers:
Question 1: What are the four evidence of evolution listed in the DO NOW section? Answer: The four evidence of evolution listed are: • F (Evidence from Fossil records) • A (Analysis of body structures (Anatomy)) • M (Analysis of biochemical material (Molecular)) • E (Embryonic similarities)
Question 2: What is the biggest change in skull anatomy that occurred from the dawn horse to the modern horse? Answer: The biggest change in skull anatomy from the dawn horse to the modern horse is an increase in the size of the skull, a shift from cusps to complex ridges on the grinding surface of the premolars and molars, elongation of the face and of the space between the incisors and cheek teeth, an anterior shift of the cheek teeth so they lie forward of the eye, and a deep lower jaw bone.
Question 3: What is the biggest change in leg anatomy that occurred from the dawn horse to the modern horse? Answer: The biggest change in leg anatomy from the dawn horse to the modern horse is the reduction and loss of the side toes, and the development of a single hoof.
Question 4: What physical similarities exist between each of the embryos? Answer: The physical similarities between each of the embryos include a same basic shape, circular spots (eyes), an underbelly, tails, and tiny bumps on the underside, and a hole for an ear.
Question 5: Does examination of vertebrate embryos suggest an evolutionary relationship? Answer: Yes, examination of vertebrate embryos suggests an evolutionary relationship because all vertebrate embryos pass through stages in which they have similar physical characteristics, such as gill pouches and tails.
Question 6: What is the difference between homologous and analogous structures? Answer: Homologous structures are similar structures that related organisms share from a common ancestor, while analogous structures have different anatomies but similar functions, seen in organisms that are not necessarily closely related but live in similar environments and have similar adaptations.
Question 7: Do birds and insects share any structural similarities that would suggest they are closely related taxonomically? Answer: No, birds and insects do not share any structural similarities that would suggest they are closely related taxonomically.
Question 8: What are vestigial structures? Answer: Vestigial structures are body structures and organs that have gradually lost their function through time, due to gradual changes.

Main content in the worksheet:
This worksheet contains information that there is no proof that evolution ever happened. This statement is incorrect, and I would like to provide some facts to your readers about how scientists know that evolution has happened. Evolution refers to the process of change over time, where species change and develop over generations through natural selection. One of the primary ways that scientists know that evolution has happened is through comparative anatomy.
Comparative anatomy is the study of different species’ structures and how they are related to one another. For example, humans, chimpanzees, whales, and bats all have the same bones in their arms, fins, or wings, which is an example of comparative anatomy through homologous structures. Homologous structures are similar structures that are found in different species and are derived from a common ancestor, providing evidence of evolution.
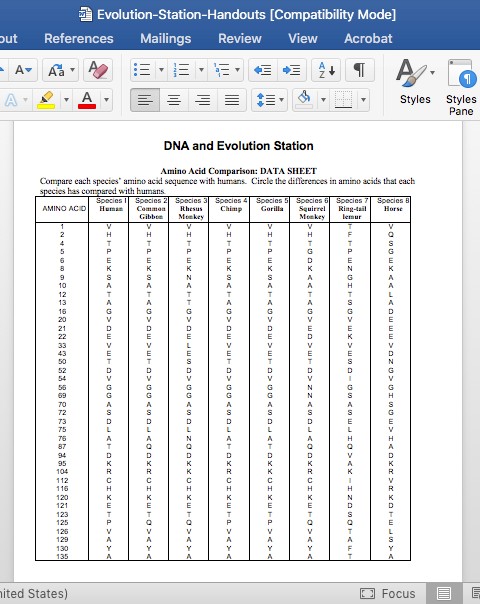
Another way that scientists know that evolution has happened is through DNA analysis. This type of analysis compares the genetic sequences of different species to determine their evolutionary relationships. For example, the human gene for muscle protein is different from monkey muscle protein in 4 places and different from a chicken’s gene in 25 places, which is evidence of evolution. The fossil record is also an important piece of evidence for evolution. Scientists find fossilized bones of animals that no longer exist today, providing evidence of species that have changed and gone extinct over time.
I assume that there is ample evidence that supports the theory of evolution, and it is widely accepted by the scientific community. I hope this letter provides some clarity and correct information to your readers about this important topic.
Sample Questions:
- What type of evidence is the similarity in bones among humans, chimpanzees, whales, and bats?
- What type of evidence is the fossilized bones of a huge animal that doesn’t exist today?
- What type of evidence is the difference in the human gene for muscle protein compared to monkey and chicken?
- What type of evidence is the difference in the tongue structure of honey possums and butterflies?
- What type of evidence is the presence of an appendix in humans, rabbits, and zebras?
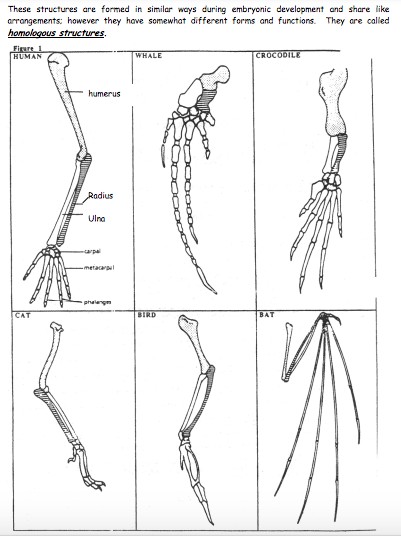
Terms used in this handout:
Biology, Unit 7-Evolution, homologous structures, analogous structures, vestigial structures, human, whale, cat, bat, bird, crocodile, butterfly wing, bird wing, penguin’s wings, leg bones of snakes, cavefish, minnow, appendix, coccyx, muscles that move ears, muscles that make hair stand up, little toe, wisdom teeth, fin of a fish, flipper of a whale, evidence of evolutionary relationships.
Sample Questions found in the handout:
- What are homologous structures?
- What are analogous structures?
- What are vestigial structures?
- What is the significance of homologous structures in evolution theory?
- What is the function of each structure in the animals: human, whale, cat, bat, bird, and crocodile?
- Are the bones arranged in a similar way in each animal?
- What function do the butterfly wing and the bird wing share?
- How are the butterfly wing and the bird wing different?
- Do birds and insects share any structural similarities that would suggest they are closely related taxonomically?
- Why is eyesight not an important adaptation to life in a cave?
- What has become the most important adaptation of the cave fish?
- What about the internal structure of the cavefish and minnow suggest common ancestry?
- Suggest a possible function for each of the vestigial structures in humans.
- Why are homologous structures evidence of evolutionary relationships?
- What is the evolutionary relationship between the fin of a fish and the flipper of a whale?
- List two structures that you think are vestigial and explain why.
- Re-define the three different types of evidence for evolution in your own words.
Editable Version: Doc Format
Background: Darwin used evidence gathered from paleontology, geology, population studies, economics, empirical evidence, and others to formulate his theory of “Descent with Modification”. Developing the sound theory was the first step but evolution has been under constant scrutiny. There are many sources of evidence to support evolution but these six are the major categories we will focus on.
- The Fossil Record
- Biogeography
- Developmental biology
- Anatomy
- Natural Selection is observed
- Biochemistry
Objective: To investigate fossils, biogeography, developmental biology, homologous, analogous, and vestigial structures, and biochemistry to determine their significance in evolutionary history.
Background
Much evidence has been found to indicate that living things have evolved or changed gradually during their natural history. The study of fossils as well as work in embryology, biochemistry and comparative anatomy provides evidence for evolution.
Objective
In this lab you will learn about homologous, analogous and vestigial structures and their significance in evolution theory.
TAKS: The student knows the theory of biological evolution. The student is expected to identify evidence of change in species using fossils, DNA sequences, anatomical similarities, physiological similarities, and embryology.
Big Questions:
Why are homologous structures used as evidence of evolution?
How can vestigial structures be explained by natural selection?

Sample Instruction:
- Carefully examine the drawings of the bones
- Look for similarities among the various animals.
- Color each part of the human arm a different color
- Describe the function of each structure
- Choose a color for each bone on the human forelimb and color the corresponding bone in the other organisms the same color
- Examine the butterfly wing and the bird wing
- Explain why eyesight is not an important adaptation to life in a cave
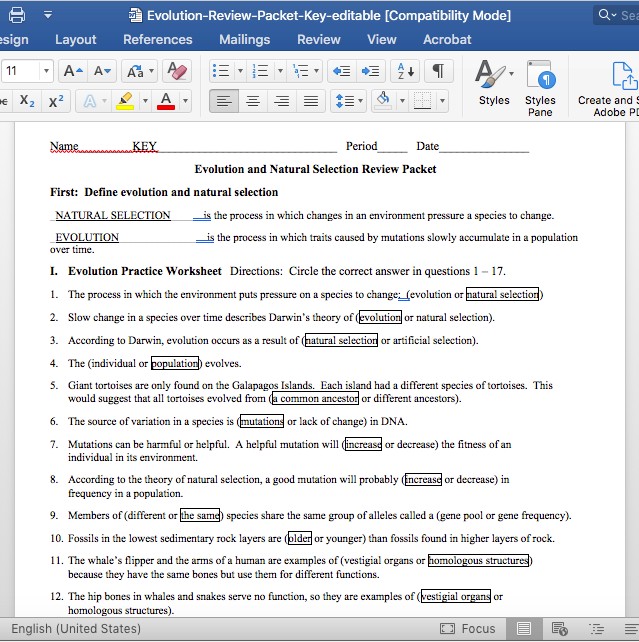
Sample Questions, choose correct answer:
- The process in which the environment puts pressure on a species to change: (evolution or natural selection)
- Slow change in a species over time describes Darwin’s theory of (evolution or natural selection).
- According to Darwin, evolution occurs as a result of (natural selection or artificial selection).
- The (individual or population) evolves.
- Giant tortoises are only found on the Galapagos Islands. Each island had a different species of tortoises. This
would suggest that all tortoises evolved from (a common ancestor or different ancestors). - The source of variation in a species is (mutations or lack of change) in DNA.
- Mutations can be harmful or helpful. A helpful mutation will (increase or decrease) the fitness of an
individual in its environment. - According to the theory of natural selection, a good mutation will probably (increase or decrease) in
frequency in a population. - Members of (different or the same) species share the same group of alleles called a (gene pool or gene frequency).
- Fossils in the lowest sedimentary rock layers are (older or younger) than fossils found in higher layers of rock.
- The whale’s flipper and the arms of a human are examples of (vestigial organs or homologous structures)
because they have the same bones but use them for different functions. - The hip bones in whales and snakes serve no function, so they are examples of (vestigial organs or
homologous structures). - (Vestigial organs or Homologous structures) show that two species evolved from a common ancestor.
- All vertebrate embryos are (alike or not alike) in that they all have similar patterns of development.
- An ancestral flock of finches flew from South America to the Galapagos Islands. They spread out and adapted to all the different environments on the islands. This is an example of (evolution or artificial selection) due to (behavioral or geographic) isolation.
- Mountains, volcanic eruptions, and large bodies of water are examples of (geographic or reproductive) barriers that can isolate populations.
- Two groups that are geographically isolated for long periods of time tend to become reproductively isolated due to (choice or mutations).
Why you need these Evidence of Evolution Worksheet
Have you ever wondered how species change over time and why they’re different from each other? Evolution is the answer. Evolution is the process by which species change over generations. The study of evolution is fascinating and can help us understand the mysteries of life on Earth.
And if you’re interested in learning about evolution, then you’ll love studying about the evidence of evolution. This topic covers all the ways in which scientists can determine how species have changed over time. One fun way to study this is through an evidence of evolution worksheet.
An Evidence of Evolution Worksheet is a great tool to help you learn about the different pieces of evidence that scientists use to support the theory of evolution. It usually includes questions, puzzles, or activities that help you understand the various pieces of evidence and how they support the theory.
The worksheet can also help you learn about comparative anatomy. Comparative anatomy is the study of how different species are related based on their anatomy. For example, by comparing the anatomy of a human and a chimpanzee, scientists can see that they’re closely related.
And if you’re looking for a Darwin Theory of Evolution PDF Answer Key, there are resources available that can help you understand the theory of evolution and how it works.
Finally, if you want to test your knowledge of evolution, you can take an Evidence of Evolution Quiz PDF. These quizzes are a fun way to see how much you’ve learned about evolution and the evidence that supports it.
As for my last suggestion, if you’re interested in learning about evolution, then studying an Evidence of Evolution Worksheet is a great way to start. You’ll learn about the different pieces of evidence that support the theory of evolution and how they fit together. And by using resources like the Evolution Worksheet Answer Key, the Darwin Theory of Evolution PDF Answer Key, and the Evidence of Evolution Quiz PDF, you’ll be able to test your knowledge and see how much you’ve learned.”
MORE:
12 FREE Printable Periodic Tables PDF, PNG, SVG HD
The Cell Cycle Coloring Worksheet
FREE Digital Art
FREE Reading Websites